How Do BIN / INN Numbers Work? (And Why They Matter)
Understanding the Bank Identification Numbers, Luhn algorithm, and ISO/IEC 7812-1:2017 standard that power every credit card transaction worldwide.

Summary: BIN/INN numbers are the first 6-8 digits of every credit and debit card, serving as unique identifiers for card-issuing institutions. This comprehensive guide explains how BIN numbers work, their role in the global payment ecosystem, the Luhn algorithm for card validation, and the ISO/IEC 7812-1:2017 international standard that governs card numbering worldwide.
What is a BIN / INN? (And Why Should You Care?)
Every credit or debit card comes with a unique number printed right on the front. But did you know that the first few digits of your card tell a story? These digits are far more than random numbers they're a sophisticated identification system that powers the global payment infrastructure processing trillions of dollars annually.
BIN stands for Bank Identification Number. INN means Issuer Identification Number. They're two names for the same thing, with the industry gradually transitioning to the more accurate term "IIN" since non-bank institutions (like fintech companies) can also issue payment cards. Here's why they matter:
- The BIN/INN comprises the first 6 to 8 digits of your payment card number.
- It uniquely identifies the financial institution or card issuer (bank, credit union, fintech, etc.).
- It reveals the card network (Visa, Mastercard, American Express, Discover, etc.).
- It indicates the card type (credit, debit, prepaid, corporate, gift card).
- It provides geographic information about the issuing country or region.
- It enables instant fraud detection and transaction routing for merchants.
- It facilitates compliance with payment industry regulations and standards.
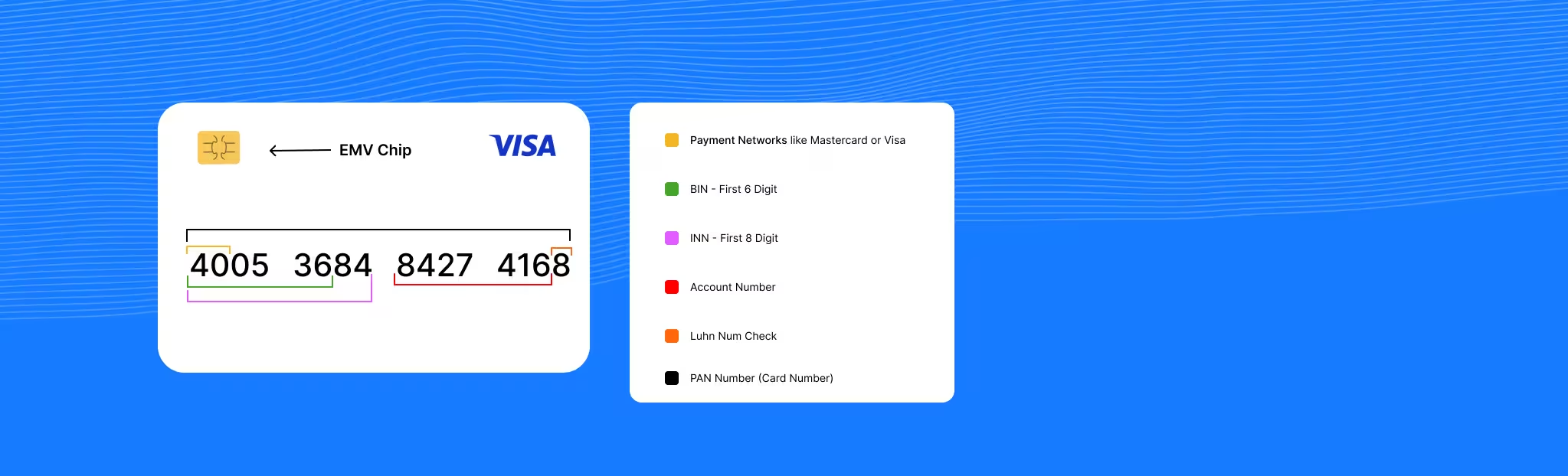
How Do BIN / INN Numbers Work?
Understanding the structure of payment card numbers is essential for anyone working in payments, e-commerce, or financial technology. Let's break it down with a typical 16-digit card number:
Example: 4532 1234 5678 9010
- The first 6-8 digits (453212): This is the BIN/IIN, which identifies the card issuer and network. In this example, the '4' indicates Visa, and the complete 6-digit sequence identifies the specific issuing bank.
- The middle digits (34567890): These digits form the individual account identifier (IAI), uniquely identifying the cardholder's account within the issuing institution. This section can vary in length depending on the total card number length.
- The last digit (0): This is the Luhn check digit, a calculated value used to validate the entire card number and detect errors or typos.
Important Note: While traditional BIN numbers were 6 digits, the payment industry expanded to 8-digit BINs in April 2017 due to the exhaustion of 6-digit combinations. Modern payment systems must support both 6 and 8-digit BIN formats to ensure compatibility across all card types and issuers.

The Global Standard: ISO/IEC 7812-1:2017
Ever wonder how all banks and cards around the world agree on what those numbers mean? That's thanks to a global rulebook called ISO/IEC 7812-1:2017, the international standard titled "Identification cards Identification of issuers Part 1: Numbering system."
Published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), this standard is maintained by technical committee ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 17. It provides the foundation for interoperability in the global payments ecosystem.
Key provisions of ISO/IEC 7812-1:2017 include:
- Card Number Length: Specifies that Primary Account Numbers (PANs) must be between 8 and 19 digits long, though most consumer cards use 16 digits.
- Major Industry Identifier (MII): The first digit identifies the card's industry category (banking, airlines, travel, etc.).
- Issuer Identification Number (IIN): The first 6-8 digits uniquely identify the card issuing institution globally.
- Check Digit Algorithm: Mandates the use of the Luhn algorithm (ISO/IEC 7812-1) for the final digit.
- Registration System: Establishes procedures for issuing institutions to register their IIN ranges with ISO.
- Global Uniqueness: Ensures no two issuers receive the same IIN, preventing conflicts worldwide.
This standardization is crucial: it means whether you're using a card in Paris, Texas or Paris, France, Tokyo or Toronto, everyone's playing by the same rules. A merchant in Australia can instantly validate and process a card issued in Argentina, thanks to this universal standard.
The 2017 revision specifically addressed the expansion from 6 to 8-digit IINs, providing additional capacity as the number of card-issuing institutions worldwide continues to grow.
The Luhn Algorithm: The Card's Secret Security Check
Ever wonder how your bank knows if you typed your card number wrong? How does an e-commerce website instantly tell you "Invalid card number" before even contacting your bank?
Meet the Luhn algorithm (also known as the "modulus 10" or "mod 10" algorithm), invented by IBM scientist Hans Peter Luhn in 1954! It's an elegant mathematical checksum formula used to validate card numbers. While it's not cryptographic security, it's exceptionally effective at catching typos, transposed digits, and other input errors catching about 98% of single-digit errors and most common transcription mistakes.
How the Luhn Algorithm Works:
- Start from the right: Begin with the last digit (check digit) and move left through the card number.
- Double every second digit: Starting from the second-to-last digit, double every alternate digit as you move left.
- Handle numbers over 9: If doubling a digit results in a number greater than 9, subtract 9 from it (or equivalently, sum the two digits).
- Sum all digits: Add up all the digits, including those you didn't double.
- Check divisibility: If the total sum is divisible by 10 (ends in 0), the card number is valid!
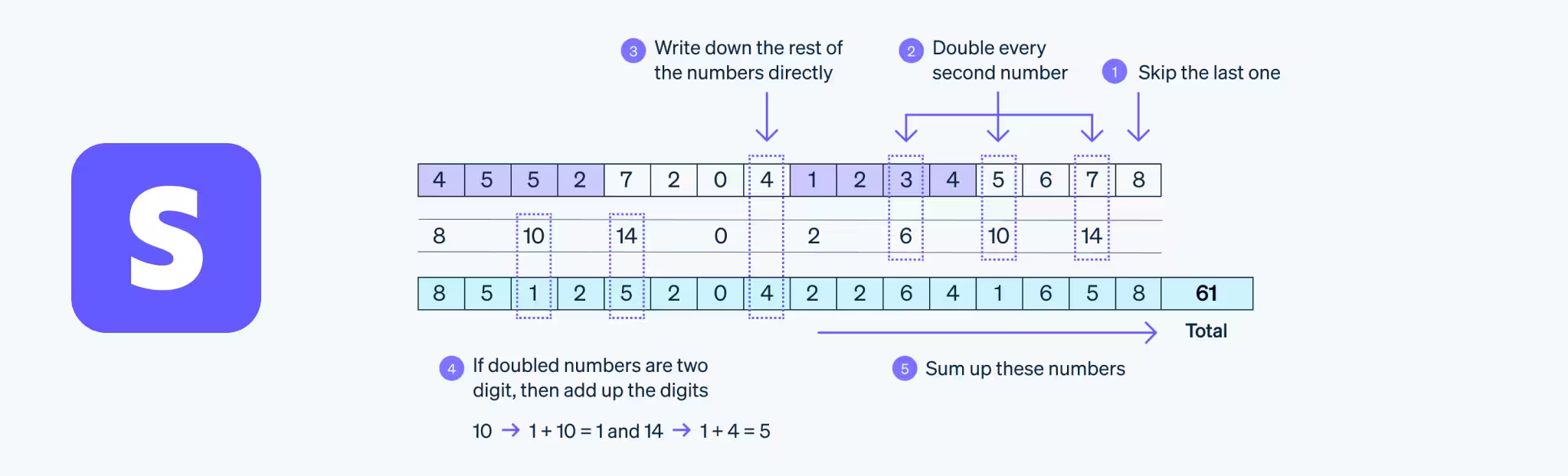
Luhn Algorithm Example: Validating 4532 1234 5678 9010
Step 1: Write the digits and identify which to double (every second digit from right):
4 5 3 2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 0
Double these: ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
Step 2: Double the marked digits:
4→8, 3→6, 1→2, 3→6, 5→10, 7→14, 9→18, 1→2
Step 3: For numbers over 9, subtract 9:
10→1, 14→5, 18→9
Step 4: Sum all digits:
8+5+6+2+2+2+6+4+1+6+5+8+9+0+2+0 = 66
Step 5: Check if divisible by 10:
66 mod 10 = 6 (not 0), so this example would be invalid
Note: This is a demonstrative example. Real card numbers would have the correct check digit calculated to ensure the sum is divisible by 10.
Why Does This Matter? The Real-World Impact
The BIN/IIN system and its associated standards aren't just technical details they're critical infrastructure supporting the global economy. Here's the real-world impact:
- Security & Fraud Prevention: BIN/INN lookup and Luhn validation help spot fake or mistyped cards instantly. According to payment industry data, these basic checks prevent billions of dollars in fraudulent transactions annually. The Luhn algorithm alone catches approximately 98% of accidental errors before transactions are even submitted to payment processors, reducing unnecessary processing costs and improving user experience.
- Transaction Speed & Efficiency: Merchants can instantly identify the card issuer, network, and type in milliseconds. This enables real-time decision-making for transaction routing, reducing processing time by 200-300 milliseconds per transaction. At scale, this translates to processing millions more transactions per day across the global payment infrastructure.
- Global Interoperability: With ISO/IEC 7812-1:2017 standardization, your card works seamlessly in over 200 countries and territories worldwide. The payment card industry processes over 500 billion transactions annually, and this universal standard makes it all possible.
- Cost Reduction: By enabling instant validation and routing, BIN systems reduce declined transactions (which cost merchants $118 billion annually in lost revenue), minimize manual review requirements, and decrease customer service inquiries related to payment issues.
- Regulatory Compliance: BIN data helps businesses comply with regulations like PSD2 in Europe, Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) requirements, and regional payment regulations by identifying card characteristics instantly.
- Business Intelligence: BIN analytics provide valuable insights into customer payment preferences, regional trends, and market opportunities, helping businesses optimize their payment strategies and reduce costs.
The Bottom Line: Every time you make a purchase whether online or in-store BIN/IIN systems work invisibly in the background, ensuring your payment is secure, routed correctly, and processed efficiently. For businesses processing payments, understanding and leveraging BIN data is no longer optional it's essential for competitive operations in the modern payment landscape.
Real-World Applications of BIN/INN Lookup
Understanding BIN/IIN numbers isn't just academic it has practical applications across the payment industry:
- Fraud Prevention: By instantly identifying the issuing bank and card type, merchants can flag suspicious transactions from high-risk regions or card types.
- Payment Routing: Different card networks (Visa, Mastercard, Amex) have different processing fees. BIN lookup helps route transactions efficiently.
- Card Type Detection: Instantly determine if a card is credit, debit, prepaid, or corporate crucial for businesses with different acceptance policies.
- Geographic Analysis: BIN data reveals the country of issuance, helping businesses assess transaction risk and comply with regional regulations.
- Customer Experience: Auto-fill card type icons and optimize checkout flows based on the detected card network.
Understanding the Complete Card Number Structure
Let's examine a complete 16-digit card number in detail:
Card Number Breakdown: 4532 1234 5678 9010
- First Digit (4): Major Industry Identifier (MII) - 4 = Banking and financial
- First 6 Digits (453212): BIN/IIN - Identifies the issuing institution
- Digits 7-15 (34567890): Individual account identifier
- Last Digit (0): Luhn check digit for validation
Major Industry Identifiers (MII):
- 0 - ISO/TC 68 and other industry assignments
- 1 - Airlines
- 2 - Airlines and other industry assignments
- 3 - Travel and entertainment (Amex, Diners Club)
- 4 - Banking and financial (Visa)
- 5 - Banking and financial (Mastercard)
- 6 - Merchandising and banking/financial (Discover)
- 7 - Petroleum and other industry assignments
- 8 - Healthcare and telecommunications
- 9 - National assignment
Frequently Asked Questions About BIN/INN Numbers
What is a BIN/INN number?
BIN (Bank Identification Number) and IIN (Issuer Identification Number) are the first 6 to 8 digits of a credit or debit card number. They identify the institution that issued the card and the card network (Visa, Mastercard, etc). These numbers help merchants verify card authenticity and route transactions correctly.
How does the Luhn algorithm work?
The Luhn algorithm is a checksum formula used to validate credit card numbers. It works by: 1) Starting from the right, double every second digit, 2) If doubling creates a number over 9, subtract 9, 3) Sum all digits, 4) If the total ends in 0, the card number is valid. This helps catch typos and basic fraud attempts.
What is ISO/IEC 7812-1:2017?
ISO/IEC 7812-1:2017 is the international standard that defines the numbering system for identification cards. It specifies how payment card numbers should be structured, including the BIN/IIN format, account number placement, and check digit requirements. This ensures global compatibility for card payments.
Why are BIN/INN numbers important for merchants?
BIN/INN numbers are crucial for merchants because they enable: instant card type identification (credit/debit), fraud detection by verifying issuing bank, correct transaction routing to payment networks, geographic risk assessment, and compliance with payment regulations. They help reduce chargebacks and improve payment security.
How many digits are in a BIN/IIN?
Traditionally, BIN/IIN numbers were 6 digits long. However, due to the growing number of card issuers worldwide, the payment industry expanded to 8-digit BINs starting in 2017. Modern systems should support both 6 and 8-digit BIN/IIN formats for complete compatibility.
Can I use BIN lookup to detect fraud?
Yes! BIN lookup is a powerful fraud detection tool. It helps identify: mismatched card type and purchase patterns, high-risk card issuers or regions, prepaid cards used in fraudulent schemes, and inconsistencies between billing address and card origin. However, BIN lookup should be part of a comprehensive fraud prevention strategy, not the only measure.
Are BIN/INN lookups PCI compliant?
Yes, BIN/IIN lookups are PCI DSS compliant. The first 6-8 digits of a card are not considered sensitive authentication data according to PCI standards. Merchants can safely store and use BIN data for fraud prevention, analytics, and transaction routing without additional security requirements beyond standard PCI compliance.
Industry Standards and Compliance
Working with BIN/IIN data requires understanding several industry standards and compliance frameworks:
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): BIN numbers are explicitly not considered sensitive authentication data under PCI DSS. They can be stored for business purposes without requiring the same security controls as full PANs, making them valuable for analytics and fraud prevention.
- EMV Standards: Europay, Mastercard, and Visa standards govern chip card technology, which works in conjunction with BIN data for secure card-present transactions.
- Card Network Rules: Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and other networks maintain comprehensive operating regulations that govern how BIN data must be used by merchants and processors.
- ANSI Standards: American National Standards Institute provides additional standards for financial services that complement ISO/IEC 7812.
References and Standards
- ISO/IEC 7812-1:2017 - Identification cards Identification of issuers Part 1: Numbering system (International Organization for Standardization)
- ISO/IEC 7812-2:2017 - Identification cards Identification of issuers Part 2: Application and registration procedures
- PCI Security Standards Council - PCI DSS Requirements and Security Assessment Procedures
- EMVCo - EMV Payment Tokenisation Specification – Technical Framework
- Visa Core Rules and Visa Product and Service Rules - Card acceptance and processing requirements
- Mastercard Rules Manual - Operating regulations for Mastercard acceptance
- American Express Merchant Operating Guide - Requirements for American Express card acceptance
Quick Recap: Everything You Need to Know About BIN/INN Numbers
- The BIN/INN is the card's fingerprint it tells who issued the card and what network it belongs to.
- The Luhn algorithm is a quick math check to catch errors and validate card numbers.
- ISO/IEC 7812-1:2017 is the global rulebook that keeps cards standardized worldwide.
- BIN lookup powers fraud detection, payment routing, and customer experience optimization.
- Modern BINs can be 6 or 8 digits long always support both formats.
Next time you look at your card, you'll know there's a lot of clever stuff going on behind those numbers! Whether you're a developer integrating payment systems, a merchant optimizing fraud detection, or just curious about how payments work, understanding BIN/INN numbers is essential knowledge in today's digital economy.